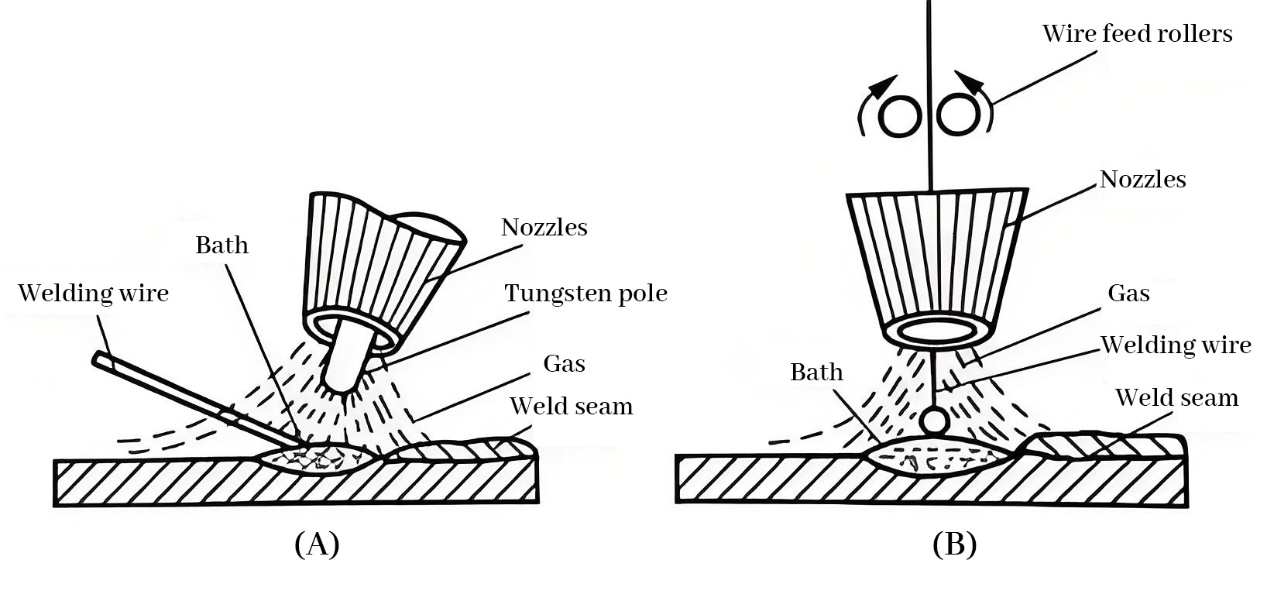
TIG welding (TIG welding, Tungsten Inert Gas welding is a kind of arc welding process using non-fused tungsten electrodes, under the protection of inert gas (mainly argon). The process is widely known for its high-quality welding results and applicable to a wide range of welding materials, especially for welding stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium and its alloys and other refractory or easy to oxidize metal materials.
Working principle of tig welding
The basic principle of tig welding is to produce an arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece, using the high temperature generated by the arc to melt the workpiece, so that it forms a welded joint. Welding process, the tungsten electrode is not involved in melting, and the inert gas (usually argon) is used to protect the arc zone and the molten pool, to prevent atmospheric oxygen, nitrogen and other contamination of the weld to ensure the quality of the weld.
Components of tig welding
1.Welding machine: used to provide current and control the power of the arc.
2. Tungsten electrode: as a non-melting electrode, its high temperature resistance, not easy to consume the characteristics are very suitable for tig welding.
3. Torch: The main tool for TIG welding, the torch contains the tungsten electrode, while inert gas flows through the torch nozzle to protect the arc and the molten pool.
4. Inert gas (argon): mainly used to protect the arc and the molten pool, to avoid contamination of the welding area by oxygen and nitrogen in the air.
5. Filler metal (optional): according to the need, may use hand-filled wire to supplement the weld material.
Advantages of tig welding
1. high welding quality: due to the protective effect of argon gas, the welding process is not easy to be oxidized, the weld is smooth, no spatter, less welding defects.
2. high welding precision: suitable for thin plate, precision parts welding, can control a small arc, providing very fine welding.
3. Multi-material applicability: Tig welding is suitable for welding a variety of materials, especially stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, nickel and its alloys and other non-ferrous metals.
4. Flexible operation: can be welded in a variety of postures, suitable for a variety of positions welding (flat welding, vertical welding, back welding, etc.).
Disadvantages of tig welding
1. slower: due to the fine operation, welding speed is relatively slow, especially in large areas or thick plate welding is not as efficient as other methods.
2. equipment complexity and high cost: the need for specialized equipment, such as tungsten electrodes, inert gas supply, etc., increasing the cost and complexity of welding.
3. high operating skill requirements: the welder’s operating skill requirements are high, beginners have greater difficulty in mastering, especially in maintaining arc stability and control of the molten pool requires a certain amount of experience.
Application of tig welding
Tig welding is widely used in the following fields because of its high precision and high quality welding effect:
1. aerospace: TIG welding is commonly used to weld high-strength metals and light alloys in aerospace, such as aluminum, magnesium alloys, titanium and so on.
2. nuclear industry: the need for high strength, corrosion resistance and high temperature performance of the material welding, such as stainless steel and nickel-based alloys.
3. automobile manufacturing: mainly used for high-precision welding of automobile parts, especially aluminum alloy body and stainless steel exhaust pipe welding.
4. petrochemical industry: tig welding is widely used in stainless steel, aluminum tanks and pipeline welding.
5. shipbuilding industry: used for welding ships in the thin plate, aluminum alloy and stainless steel parts.
Tig welding process steps
1. Preparation:
Clean the welding area and remove impurities such as grease and oxidized skin on the surface.
According to the thickness of the workpiece to choose the appropriate diameter of the tungsten electrode.
Set the appropriate welding current and argon gas flow.
2. Ignition: High-frequency arc or contact arc ignition arc, so that the arc is formed between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece.
3. Molten pool control: the welder needs to master the length and position of the arc, control the size and shape of the molten pool to ensure a uniform weld.
4. Filler metal optional): If additional weld material is required, the wire can be filled manually while the arc melts the metal.
5. Arc out and cooling: After welding is completed, slowly extinguish the arc and continue to pass argon gas for cooling to prevent oxidation of the weld and tungsten electrode.
Precautions for tig welding
1. tungsten electrode selection and grinding: tungsten electrode type and shape (tip shape) has a great impact on the arc stability, should be based on the welding material to choose the appropriate tungsten electrode (such as cerium tungsten, thorium tungsten, pure tungsten, etc.).
2. gas flow control: argon flow is too large or too small will affect the welding effect, the flow is too large may lead to gas flow turbulence, too small is not enough protection.
3. protective measures: tig welding process arc temperature is high, light radiation, welders need to wear protective masks, gloves and other protective equipment, to avoid the arc light caused by burns or damage to the eyes.
4. Molten pool temperature control: the need to always pay attention to the temperature of the molten pool in the welding process, to prevent overheating leading to deformation of the workpiece or welding defects.
Tig welding common defects
1. porosity: insufficient protective gas flow or the surface of the workpiece is not clean, may lead to the formation of porosity.
2. not fused: welding current is insufficient or improper operation, resulting in the weld and the workpiece is not completely fused.
3. Cracks: Cracks may occur when the cooling is too fast during welding or when the workpiece has too much internal stress.
TIG welding is a widely applicable process with high welding quality, which is particularly suitable for metal materials with high requirements for welding quality. However, due to its complex operation and expensive equipment, it is usually used for occasions with high requirements for weld quality. Mastering argon arc welding technology requires welders to have a wealth of experience and technical level.
Post time: Sep-30-2024