Laser cladding and welding are two different material processing technologies that differ greatly in principle, application and purpose. Watch this article will explain to you the principles, materials, applications, heat input effects, and processing of welding and cladding. Here are the main differences between the two:
Principle and Purpose
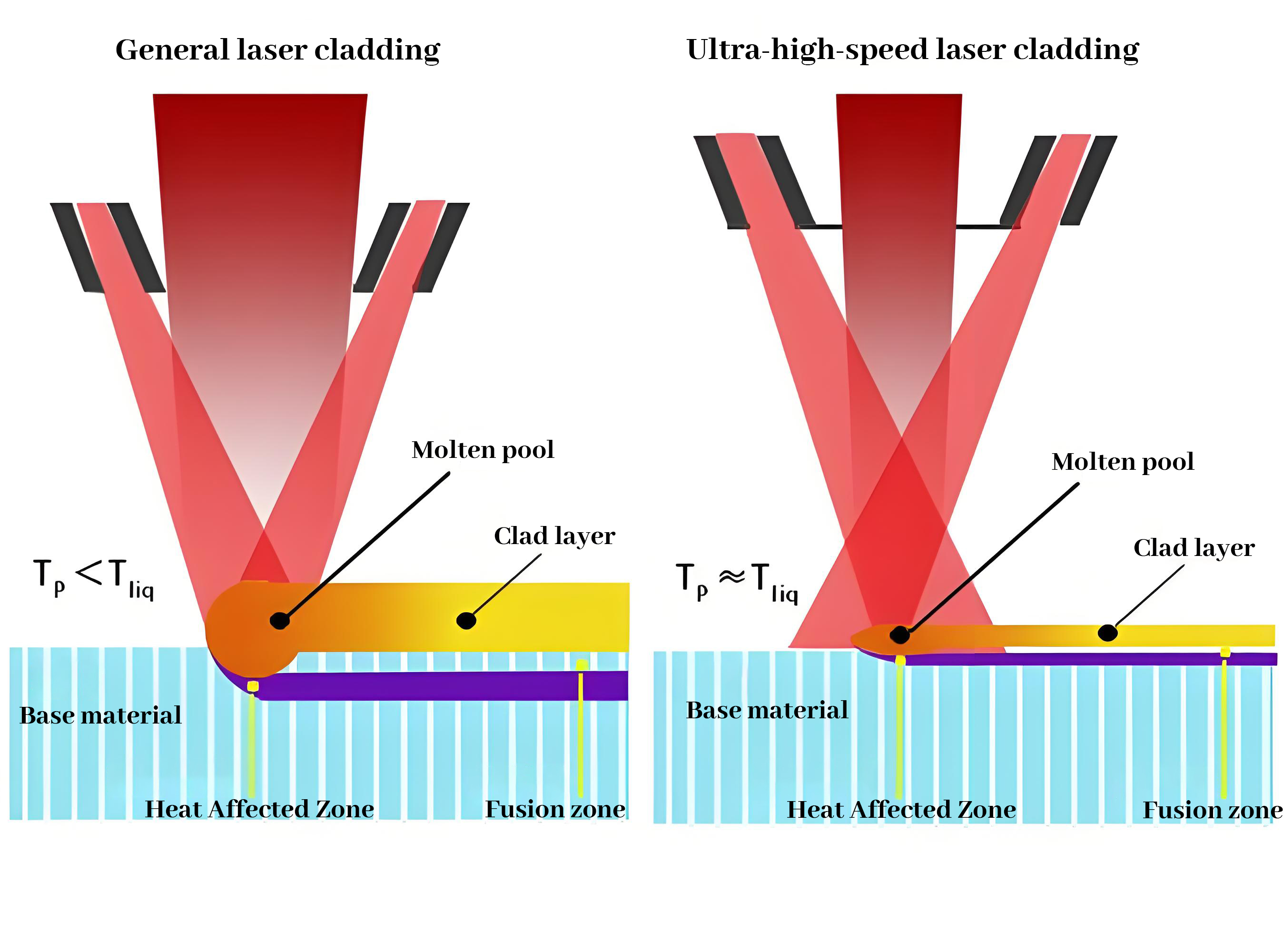
- Laser cladding:
- Laser cladding is a surface enhancement technique that utilizes a high-energy laser beam to melt the coating material and fuse it to the surface of the substrate. Its main purpose is to form a layer of coating with special properties (e.g., abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.) on the surface of the substrate to improve the surface properties of the material.
- During the cladding process, the coating material (usually a powder or filament) is melted by a laser beam, while a small portion of the surface of the substrate is also melted, forming a metallurgical bond between the coating and the substrate.
- Key purpose: To strengthen or repair the surface of the material and improve surface properties.
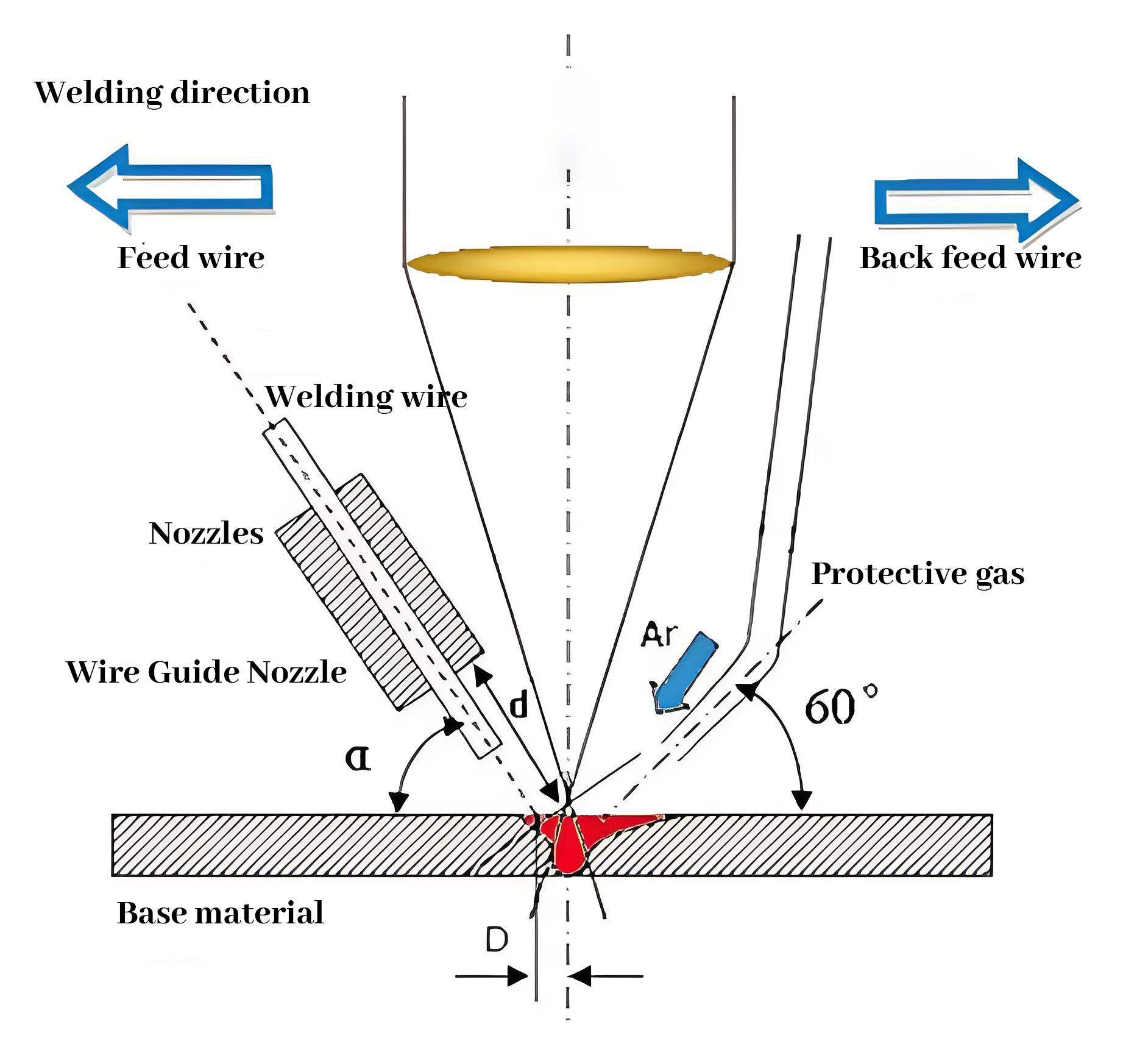
- Welding:
- Welding is the process of bringing the interface of two or more materials to a molten state by heat, pressure, or a combination of the two, culminating in a permanent connection between the materials. Welding is primarily used for structural connections, joining disparate parts together.
- Welding can use a variety of heat sources, including laser, arc, and friction.
- Key Purpose: To securely join two or more workpieces together.
Material Handling Methods
- Laser cladding:
- The coating material is usually in powder or filament form and can be metal, ceramic or composite.
- There is a clear boundary between the cladding layer and the substrate, and the thickness of the cladding can be controlled from tens of microns to several millimeters. The coating only affects the surface of the material.
- The coating only affects the surface of the material and does not affect the main properties of the substrate.
- Welding:
- Welding involves the joining of two or more monolithic workpieces, and the welding material is usually a base or filler material.
- The area of the weld is permanently bonded and the base material around the weld is subject to change (e.g. heat affected zone).
- Welding is not just about surfaces, but about forming an integrated joint by melting and solidifying two workpieces.
Application scenarios
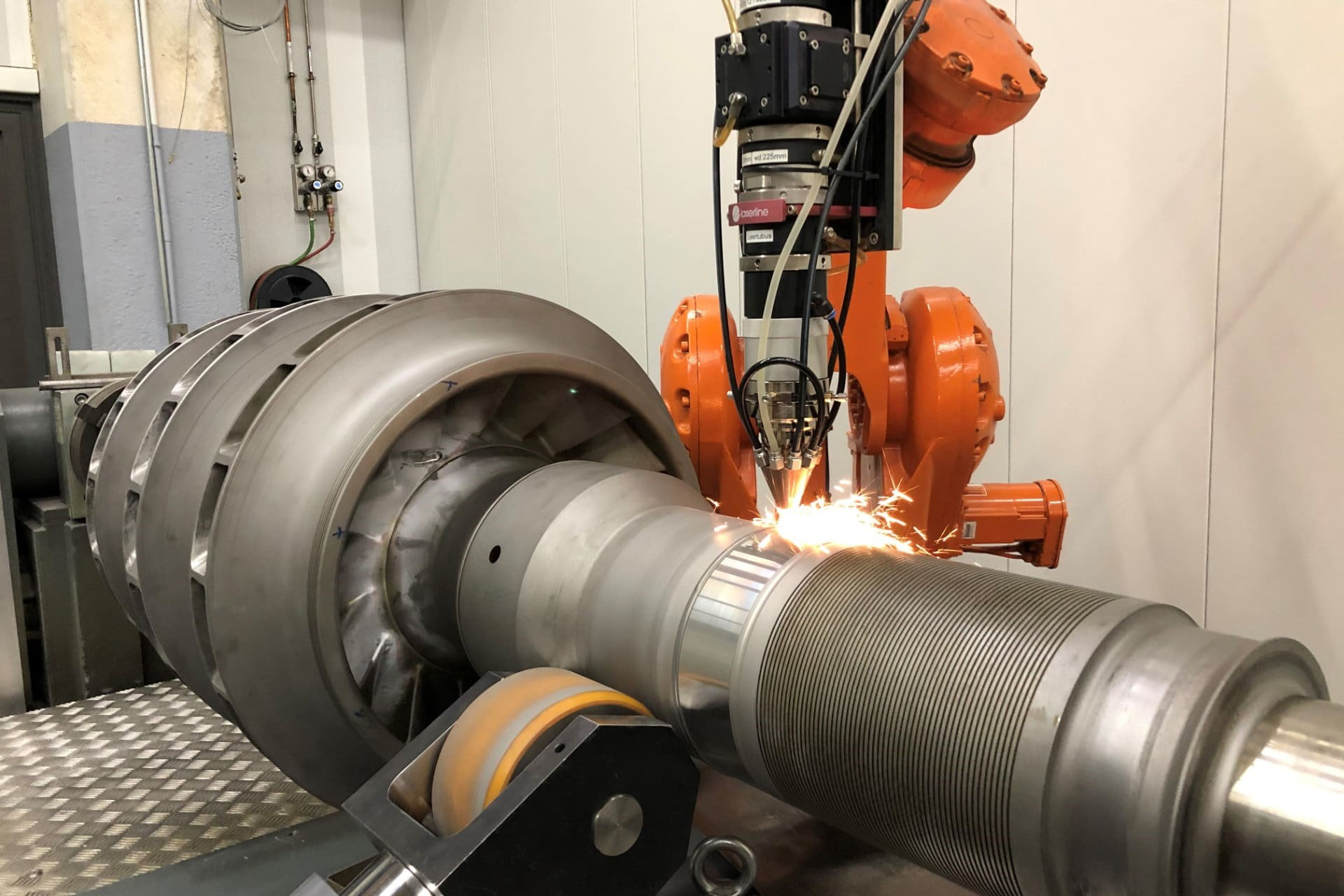
- Laser cladding:
- Commonly used for surface repair of mechanical parts, such as shafts, gears and molds. It is also used to strengthen surfaces to provide materials with better wear and corrosion resistance.
- Typical applications include the aerospace, automotive, energy and mold industries.

- Welding:
- Widely used in the manufacturing and assembly industries, especially in automotive manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding and piping where permanent connections are required.
- Common welding methods include laser welding, arc welding and gas shielded welding.
Heat input and impact
- Laser cladding:
- During the cladding process, the high energy density of the laser is concentrated in a small area, resulting in a small heat-affected area and low material deformation.
- The heat input of laser cladding is relatively low, and the impact on the base material is limited.
- Welding:
- Welding usually involves a large heat input and the base material in and around the weld area experiences thermal deformation and stress changes.
- The heat affected zone is larger and may result in changes in material properties such as hardness reduction and crack generation.
Precision and Processing Details
- Laser cladding:
- Laser cladding offers high precision, is suitable for localized microfabrication, and is controllable, enabling complex surface coating structures.
- Welding:
- The precision of welding is relatively low, especially when welding by hand or conventional arc welding. Laser welding is generally not used for fine coating of surfaces at the micron level, although it has a high degree of precision.
Key Differences
Laser cladding is primarily used for surface repair and enhancement, providing specialized properties on the surface of a material, while welding is primarily used for structural connections between materials. Cladding emphasizes the function of improving the surface of the material, while welding connects the workpieces as a whole.
Post time: Oct-10-2024