1. Electrode Arc Welding

Welding rod arc welding is the use of welding rod and workpiece established between the stable burning arc, so that the welding rod and workpiece melting, so as to obtain a solid welded joint process. During the welding process, the flux skin is constantly decomposing, melting and generating gas and slag to protect the end of the electrode, the arc, the molten pool and its surrounding area, to prevent harmful atmospheric contamination of the molten metal. Welding rod core is also under the action of the arc heat continues to melt, into the molten pool, the filler metal of the composition of the weld.
2.Submerged arc welding

Submerged arc welding (including submerged arc welding and electroslag welding, etc.) is a kind of arc in the flux layer under the burning welding method. Its inherent welding quality and stability, high welding productivity, no arc light and little fume and other advantages, so that it has become a pressure vessel, pipe manufacturing, box beams and columns and other important steel structure production in the main welding method.
3. Argon arc welding(TIG welding)

Argon arc welding (TIG welding), is the use of argon as a protective gas welding technology. Also known as argon gas shielded welding. It is in the arc welding around the argon protective gas, the air is isolated in the welding area outside, to prevent oxidation of the welding area.
Argon arc welding technology is based on the principle of ordinary arc welding, the use of argon gas protection of metal welding consumables, through the high current so that the welding consumables in the welded base material melted into a liquid state to form a molten pool, so that the welded metal and welding consumables to achieve metallurgical bonding of a welding technology, due to the high-temperature molten weld constantly fed with argon, so that the welding consumables can not be contacted with the oxygen of the air, thus preventing the oxidation of the welding consumables, and thus can be welding Stainless steel, iron hardware metal.
4. Gas welding

Gas welding, English: oxygen fuel gas welding (OFW). The use of combustible gases and combustion gases mixed combustion flame generated as a heat source, melting the weldment and welding materials to achieve inter-atomic bonding of a welding method. Flame gas is mainly oxygen, combustible gas is mainly acetylene, liquefied petroleum gas.
5. Laser welding

Laser welding is a focused laser beam as a source of energy to bombard the weldment of the heat generated by the welding method. Because the laser has refraction, focusing and other optical properties, making laser welding is very suitable for micro-parts and poor accessibility of the parts of the welding. Laser welding is also characterized by low heat input, small welding distortion, and is not affected by electromagnetic fields.
Due to the expensive laser, electro-optical conversion efficiency is low, laser welding is not yet widely used.
6. Two shielding welding
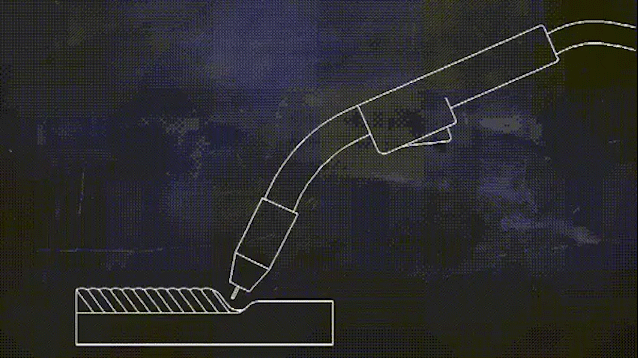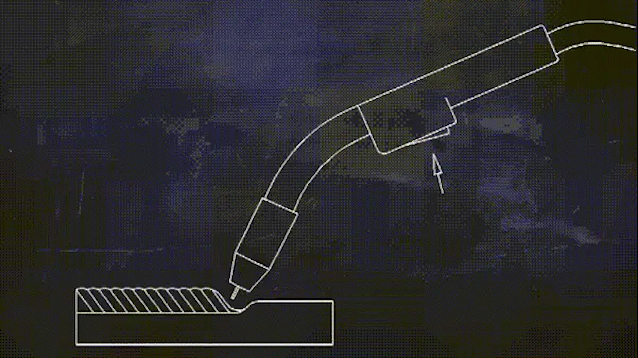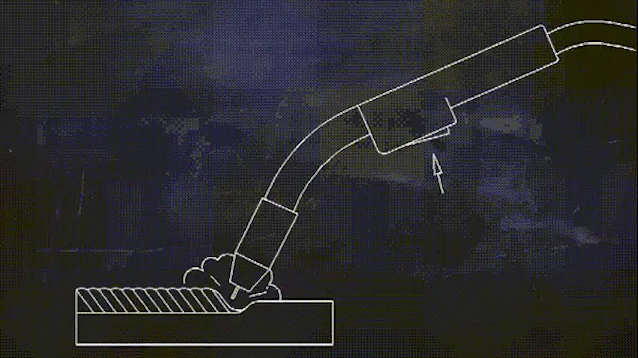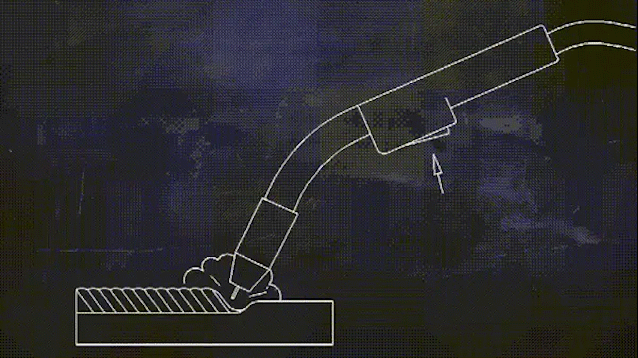
Two shielding welding (known as carbon dioxide gas shielded welding) process for low-carbon steel and low alloy high-strength steel welding of various large-scale structural steel projects, its high welding productivity, good anti-cracking performance, welding deformation is small, to adapt to the deformation of the range of large, can be thin and medium-thickness plate parts welding.
7. Friction welding
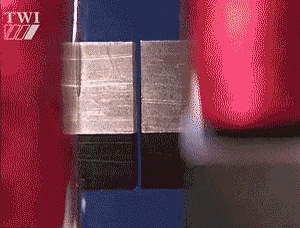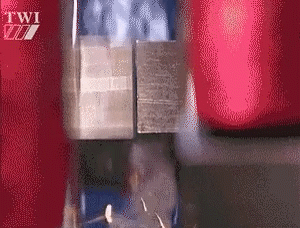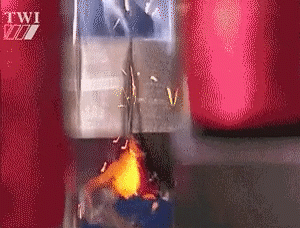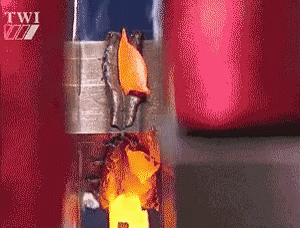
Friction welding refers to the use of heat generated by the friction of the contact surface of the workpiece as a heat source, so that the workpiece under pressure to produce plastic deformation and welding methods.
Under pressure, is under the action of constant or incremental pressure and torque, the use of welding contact between the relative motion of the end face in the friction surface and the surrounding area of the friction heat and plastic deformation heat, so that the temperature of the region and its vicinity to close to, but generally lower than the melting point of the temperature range, the material's deformation resistance is reduced, the plasticity of the interface to improve the breakage of the oxide film in the role of the top of the forging pressure, accompanied by the material to produce Plastic deformation and flow, through the interface of the molecular diffusion and recrystallization and realize the welding of solid state welding method.
8. Ultrasonic welding
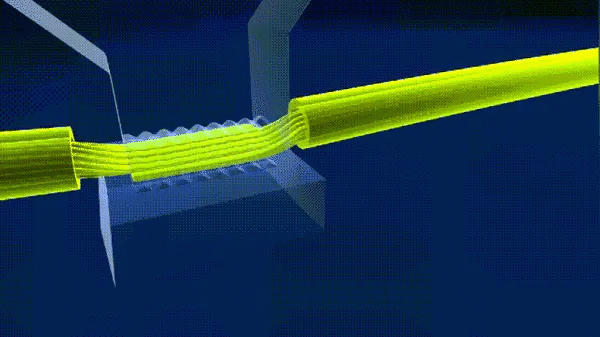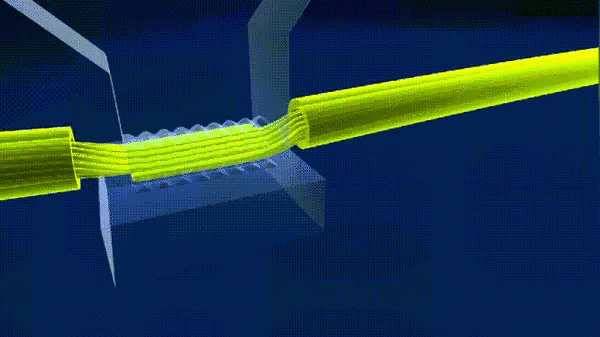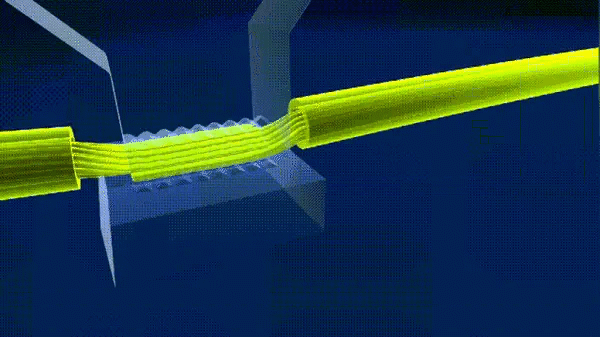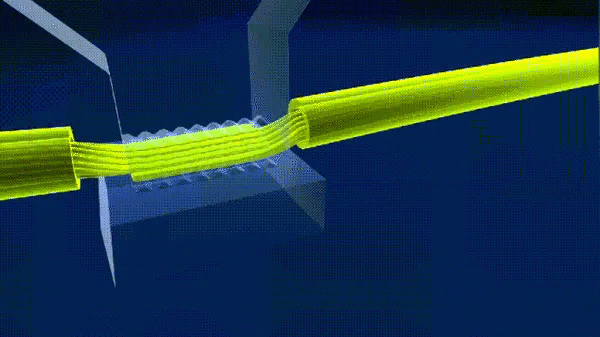
Ultrasonic welding is the use of high-frequency vibration waves transmitted to the surface of the two objects to be welded, under pressure, so that the surface of the two objects rubbing each other and the formation of fusion between molecular layers.
9.Soft brazing
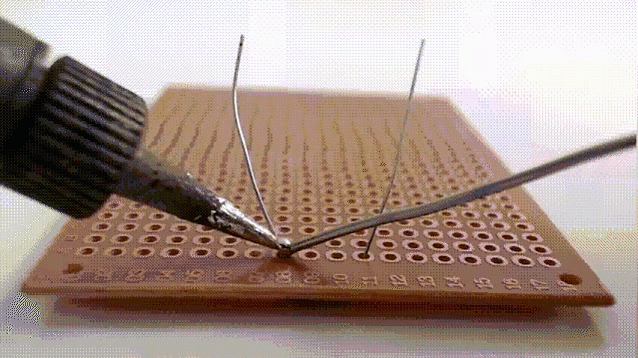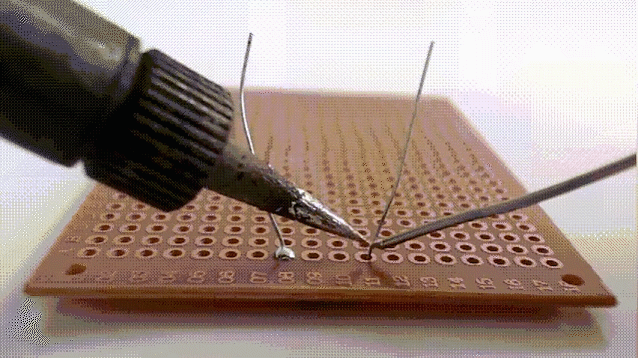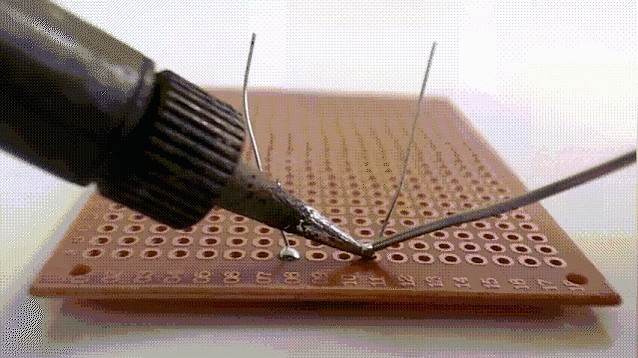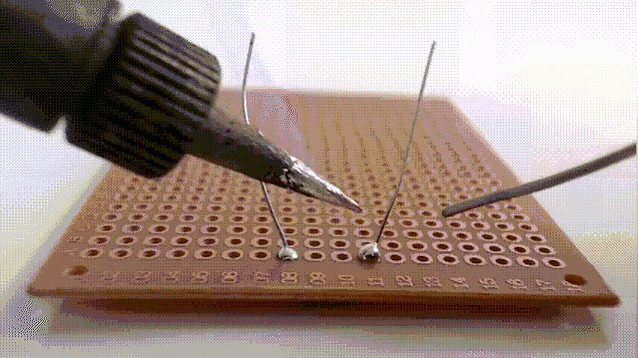
Soft brazing is a type of joining method that uses brazing material with a melting point of not more than 450°C to realize a connection by heating to a soft brazing temperature that is lower than the melting point of the base material and higher than the melting point of the brazing material. The brazing material is spread by capillary action on the surfaces of the close-fitting joint or by wetting action on the surface of the workpiece.
Soft brazing consumables are brazing consumables for soft brazing with a liquid-phase line temperature (melting point) of not more than 450°C. They are usually iron-free. Soft brazing materials are usually iron-free alloys. 450°C is the cut-off point between brazing and soft brazing. Most of the process parameters and influences involved in brazing are also applicable to soft brazing. In fact, industry terms such as soft brazing, hard brazing or silver soldering are also used to distinguish between soft brazing and brazing.
10. Hard brazing

Hard brazing is a high temperature brazing process. Most hard brazing temperatures are in the range of 1200 to 1400 F°, (much higher than soft brazing, but much lower than fusion welding). Like soft brazing, hard brazing relies on capillary action to fill the joint with brazing material. There are many different types of hard brazing alloys that can be used to weld almost any type of metal or metal alloy.
Post time: Feb-13-2025