Plasma welding, as a high-efficiency and high-precision welding technology, is widely used in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, energy and other fields. The choice of gas has a crucial impact on the quality and efficiency of plasma welding. In this paper, we will take an in-depth look at the common gases used in plasma welding and their applications.
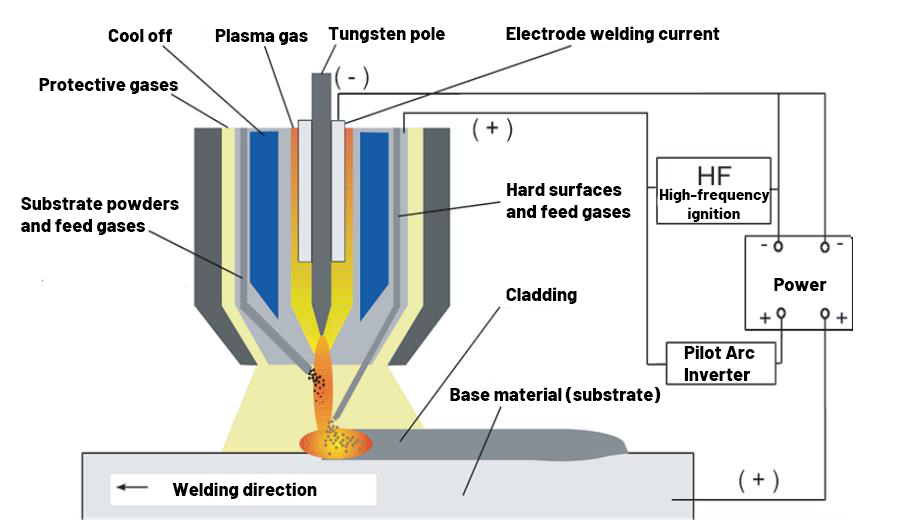
Overview of plasma welding gases
Plasma welding utilizes a high-temperature plasma arc as a heat source for welding. Gas in plasma welding plays a plasma arc formation, protection of the molten pool, affect the stability of the welding process and many other roles. Commonly used plasma welding gases include:
Argon (Ar): argon is the most commonly used plasma welding gas. It has the advantages of low ionization potential, arc stability, good protection, etc., applicable to most metal materials welding.
Helium (He): The ionization potential of helium is higher than that of argon, forming a plasma arc with higher temperature and higher energy density. Helium is suitable for welding thick plates, high melting point metals, and where greater depth of fusion is required.
Hydrogen (H₂): Hydrogen has reducing properties, which effectively removes oxides and improves weld quality. Small amounts of hydrogen (2-5%) are often mixed with argon to increase welding speed and improve weld formation.
Mixed gas: According to the welding material and process requirements, argon, helium, hydrogen can be mixed in different proportions to obtain the best welding results.
Gas Selection and Application
Materials: Different materials have different requirements for welding gases. For example, aluminum and its alloys are often welded with pure argon or argon-helium gas mixture, stainless steel welding can be used argon, argon-hydrogen gas mixture, etc..
Thickness: Pure argon is usually used for thin plate welding, while helium or argon-helium gas mixtures may be required for thick plate welding to obtain sufficient depth of fusion.
Welding Speed: Ar-He gas mixtures increase welding speed and are used when fast welding is required.
Quality Requirements: Ar-He gas mixtures or gas mixtures with a small amount of hydrogen can be used where high weld quality is required.

Plasma welding gas development trend
With the continuous development of plasma welding technology, the purity of the gas, mixing ratio, flow control and other aspects of the higher requirements. In the future, plasma welding gases will develop in the following directions:
high purity gas: Improve the purity of the gas will help reduce weld defects and improve weld quality.
Precise mixing: Precise control of the proportion of mixed gases to achieve finer control of the welding process.
Intelligent Control: Utilizing sensors and intelligent algorithms, real-time monitoring and intelligent adjustment of gas flow and composition are realized.
Conclusion
The selection and application of plasma welding gas directly affects welding quality and efficiency. Through in-depth understanding of the characteristics and application of different gases, and combined with the actual welding needs, the selection of the appropriate gas will help promote the development of plasma welding technology to meet the needs of various industries for high-quality welding.
Post time: Jun-07-2024