يُعدّ شعلة قوس نقل البلازما (PTA) العنصر الأساسي في آلة قوس نقل البلازما (PTA)، وهو مسؤول عن توليد قوس البلازما وتوصيل مسحوق السبائك بدقة إلى منطقة اللحام. يختلف هيكلها ومبدأ عملها عن شعلة اللحام التقليدية، حيث تتميز بدقة وثبات أعلى.
1. المكونات الهيكلية
الشعلة لحام PTAيتكون بشكل أساسي من الأجزاء التالية:
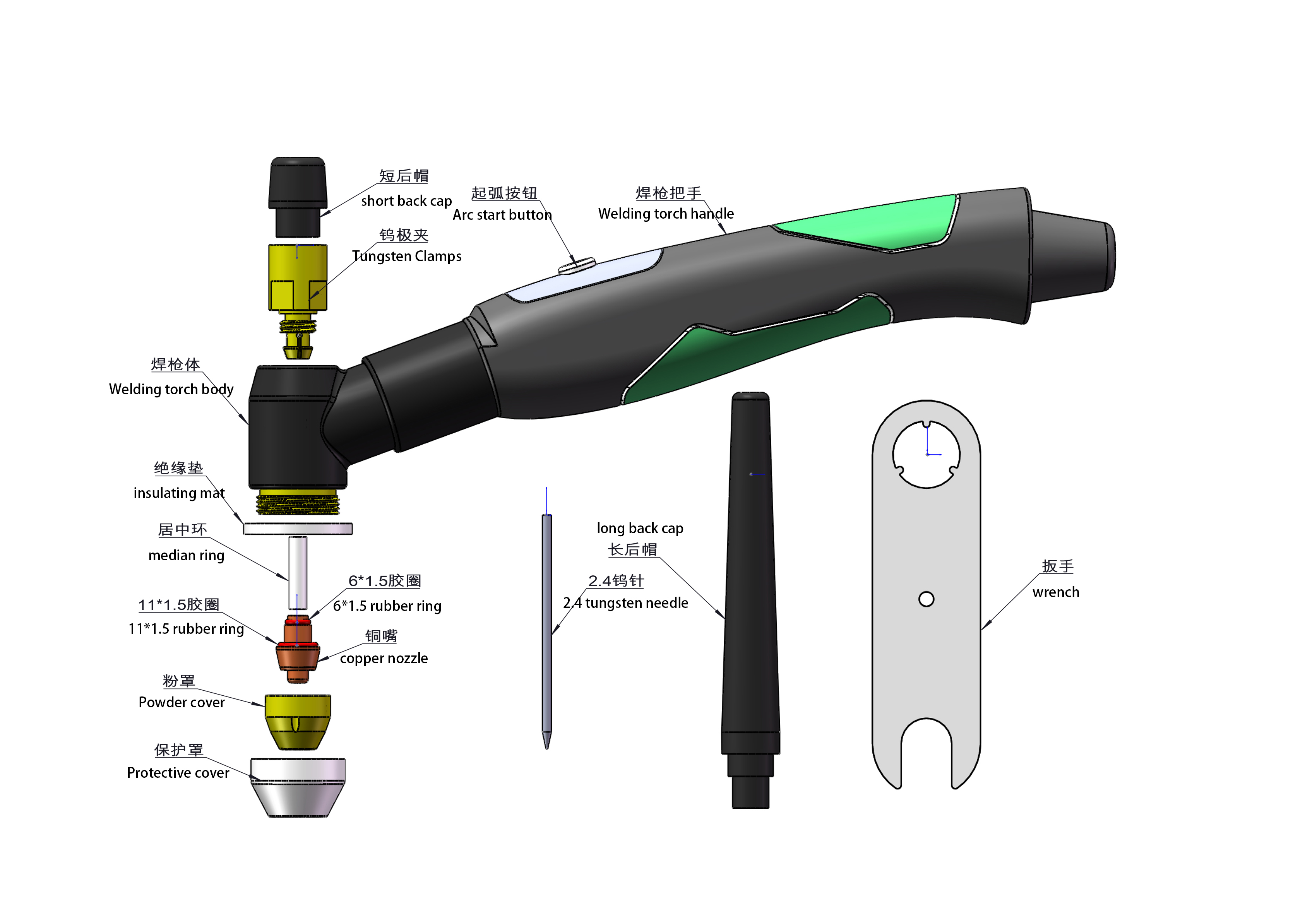
الكاثود (قطب التنغستن): هو المكون الأساسي لتوليد قوس البلازما، وهو مصنوع عادة من مادة التنغستن المقاومة لدرجات الحرارة العالية والتآكل.
الأنود (الفوهة): يوجه قوس البلازما ويركز عمود القوس، وعادة ما يكون مصنوعًا من النحاس لتحسين تبديد الحرارة.
نظام تغذية المسحوق: يستخدم لتغذية مسحوق السبائك بشكل موحد في قوس البلازما، بحيث يذوب ويترسب على سطح قطعة العمل.
قناة الغاز الواقية: يستخدم عادة الأرجون أو الهيليوم كغاز بلازما وغاز واقي لمنع الأكسدة في منطقة اللحام.
نظام التبريد: يتم استخدام تبريد المياه لضمان استقرار شعلة اللحام أثناء التشغيل في درجات حرارة عالية.
2. مبدأ العمل
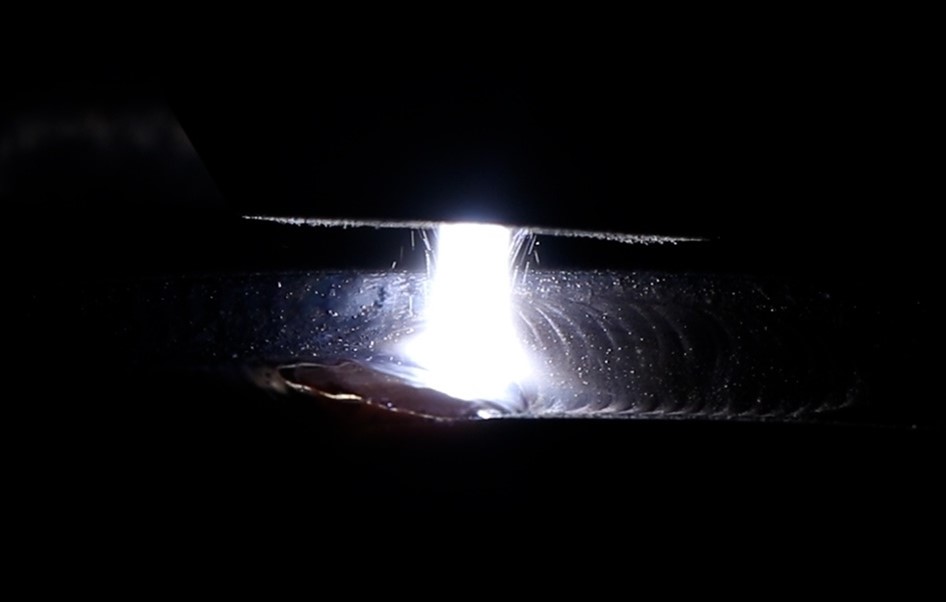

مرحلة بدء القوس: نبضة عالية التردد والجهد العالي تولد قوسًا غير قابل للنقل بين قطب التنغستن والفوهة (تيار صغير، بدء قوس مستقر).
تكوين قوس البلازما: يتم نقل غاز البلازما (مثل الأرجون) عبر الفوهة، عن طريق تأين القوس عالي الحرارة إلى بلازما عالية الطاقة، ومن خلال الفوهة إلى سطح قطعة العمل، يتم تكوين قوس النقل (القوس الرئيسي).
تغذية المسحوق والذوبان: يتم تغذية مسحوق السبائك بشكل موحد في منطقة القوس البلازمي من خلال وحدة تغذية المسحوق، ويتم إذابته على الفور ورشه على سطح قطعة العمل لتشكيل طبقة كثيفة.
الترابط المعدني: يتم ربط المسحوق المذاب معدنيًا بالمادة الأساسية لتشكيل طبقة كسوة عالية القوة ومقاومة للتآكل.
3. الميزات والمزايا

كثافة طاقة عالية: أعمدة قوسية طويلة ورقيقة، ودرجات حرارة عالية (تصل إلى 20000 درجة مئوية)، والتحكم الدقيق في عمق الذوبان وسمك الطلاء.
منطقة صغيرة متأثرة بالحرارة: تقلل من تشوه الركيزة والإجهاد الحراري، وتحسن الاستقرار الأبعادي لقطعة العمل.
معدل استخدام المواد العالية: معدل استخدام المواد المسحوقة يزيد عن 90%، وهو اقتصادي.
جودة طلاء ممتازة: طلاء كثيف، لا مسامية، قوة ربط معدنية عالية، مقاومة ممتازة للتآكل والتآكل.
4. المواد والتطبيقات الشائعة الاستخدام
مواد مسحوق السبائك: مسحوق سبائك مقاوم للتآكل ومقاوم للتآكل يعتمد على الكوبالت، والنيكل، والحديد، وكربيد التنغستن وغيرها من السبائك.
مجالات التطبيق النموذجية:
النفط والغاز: طلاءات مقاومة للتآكل والصدأ للصمامات ورؤوس الحفر وأجسام المضخات.
الآلات الهندسية: الأعمدة، اللفائف، التروس، تقوية وإصلاح سطح القالب.
الصناعة المعدنية: تسوية الأسطح وإصلاح اللفائف والقوالب ومقاعد الصمامات والأجزاء الأخرى.
5. احتياطات الاستخدام
حماية القطب الكهربائي التنغستن: منع الأكسدة والاحتراق، وإطالة عمر القطب الكهربائي.
تبريد الفوهة: الحفاظ على تأثير تبريد الماء الجيد لتجنب الضرر الناتج عن ارتفاع درجة حرارة الفوهة.
استقرار تغذية المسحوق: ضمان تغذية المسحوق بشكل متساوٍ لتجنب سمك الطلاء غير المتساوي أو عيوب الخبث.
حماية السلامة: درجة حرارة عالية، تشغيل عالي الجهد، يجب أن تكون مجهزة بأقنعة واقية وقفازات ومعدات سلامة أخرى.
6. مقارنة مع طرق اللحام الأخرى
مع لحام القوس البلازمي (PAW): يتم استخدام لحام PTA بشكل أساسي لتغليف وتقوية الأسطح، بينما يتم استخدام PAW بشكل أساسي في اللحام بالاختراق.
المقارنة مع سطح الليزر: لحام PTA أرخص ويمكن تطبيقه على مجموعة أوسع من المواد؛ ومع ذلك، فإن سطح الليزر لديه منطقة أصغر متأثرة بالحرارة ودقة أعلى.
مع رش البلازما: لحام PTA هو رابطة معدنية، قوة طلاء عالية؛ رش البلازما هو رابطة ميكانيكية، مناسبة لطلاء طبقة رقيقة.
وقت النشر: ١٩ فبراير ٢٠٢٥